A Termination Multiplexer (TM) is a device whose main function is to multiplex multiple low-speed signals into one high-speed signal, or to split one high-speed signal into multiple low-speed signals. This device plays an important role in the SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) network and is one of the main network units of the SDH network.
The main functions of the terminal multiplexer include:
Signal conversion: multiplexing multiple low-speed signals (such as T1/E1, FDDI and Ethernet) into a high-speed signal (such as STM-1 or STM-4), or splitting a high-speed signal into multiple low-speed signals.
Signal transmission: completing the conversion from electrical signal STM-N to optical carrier OC-N. The role of terminal multiplexers in SDH networks:
In SDH networks, terminal multiplexers and other network units (such as digital cross-connect devices DXC, add/drop multiplexers ADM, and regeneration repeaters REG) together form a complete SDH network. The terminal multiplexer is located at the terminal station of the chain network in the transmission network. It has only one line side direction and can complete the function of up and down branch signals. 2.
In short, the terminal multiplexer plays a key role in the SDH network. By multiplexing and demultiplexing signals, efficient network transmission and management are achieved.
Parameter:
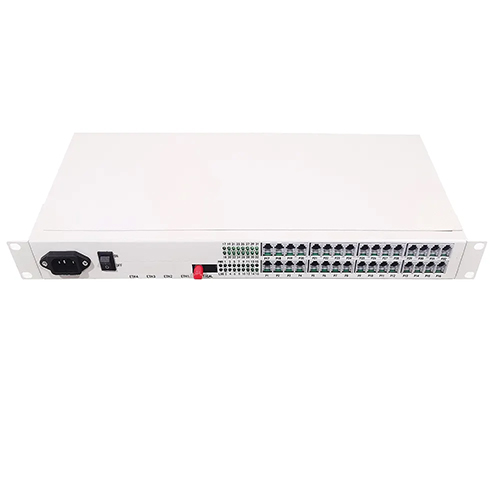
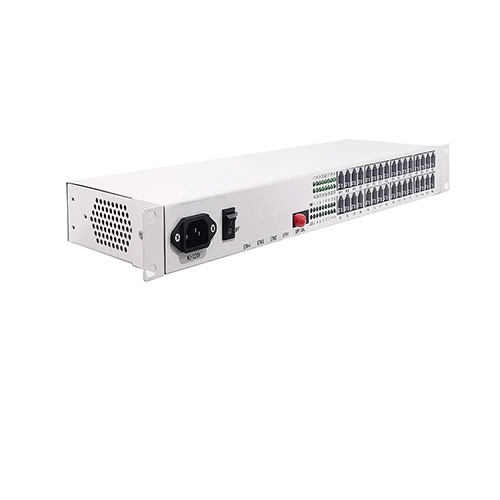
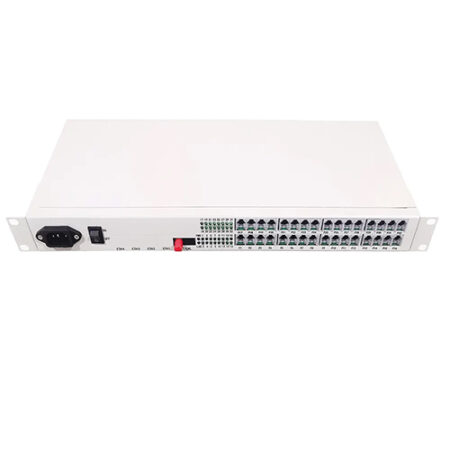
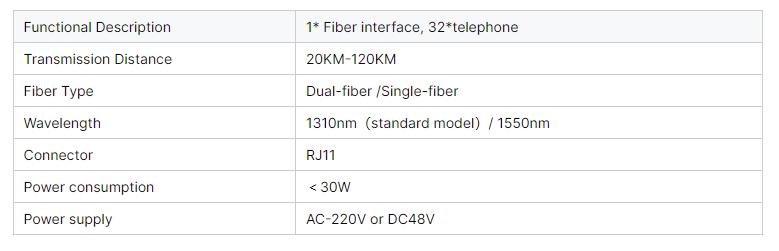
















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.